Archeological Sites
11 Sites
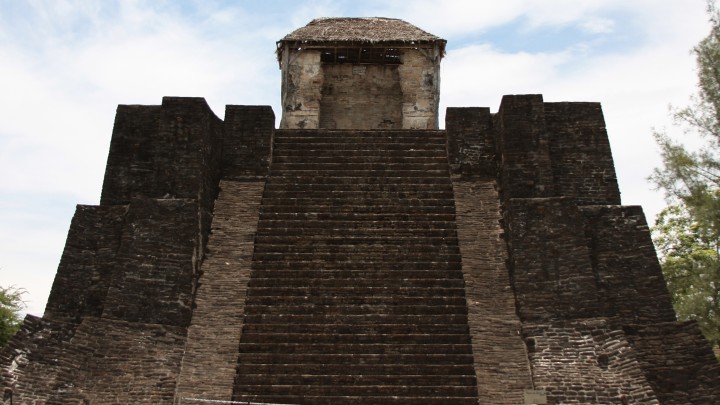
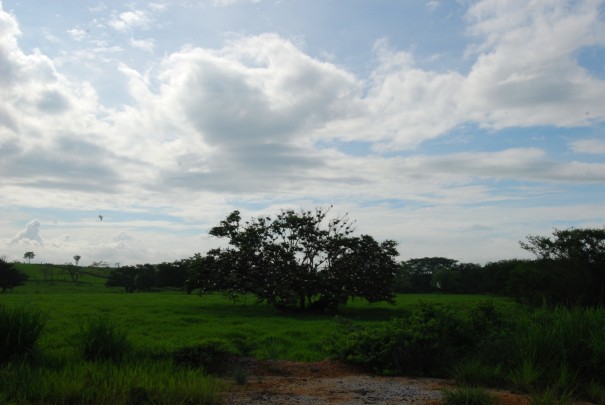
An ancient Huastec town, one of the most important sites on the Gulf of Mexico, its material remains show the influence of Maya, Toltec and Mexica cultures, at different stages of its history. It has a magnificent pyramid topped by a temple.
Veracruz
Golfo
1870
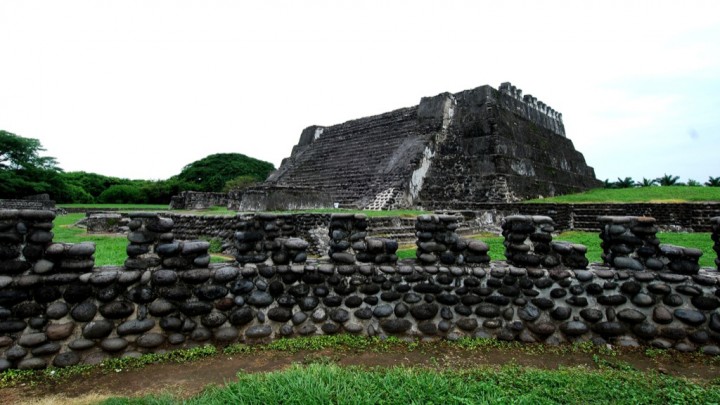
This powerful Totonac capital once dominated a large area of present day Veracruz and the north of the state of Puebla. Temples, palaces, plazas and fortifications testify to its importance as a political and religious center. Subjugated by the Mexica empire, it allied itself with Hernán Cortés to defeat Moctezuma.
Veracruz
Golfo
1871
A Totonac city with a 3,000 year history in a very damp location, where the buildings are very tall and the plazas and ballcourts are wide. The are indications of a cult to Tezcatlipoca, the smoky black mirror. It was a great exporter of colorful bird feathers.
Veracruz
Golfo
1872
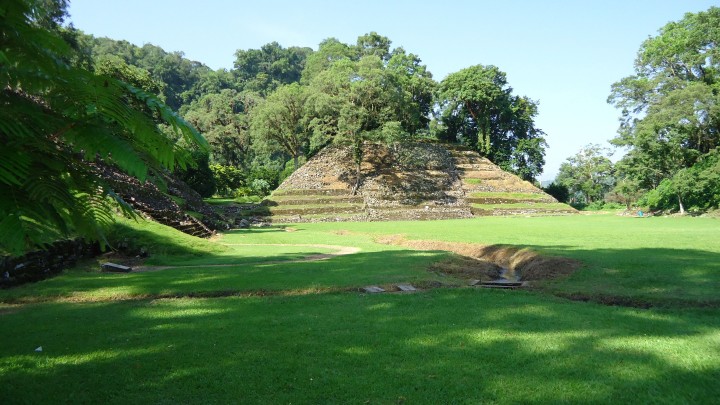
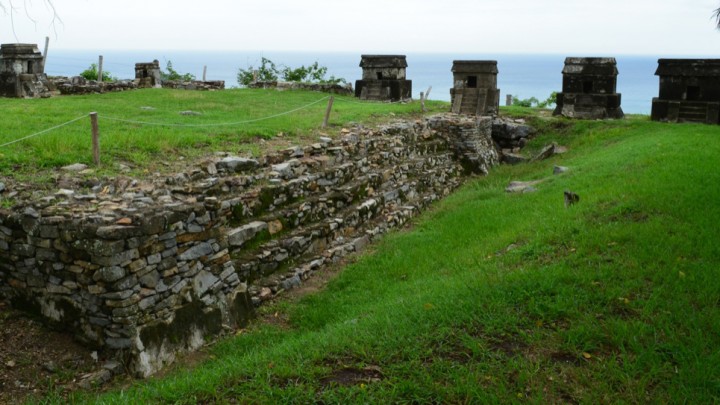
A Totonac city founded 800 years ago, its emergence coincides with the fall of El Tajín. Giving the impression of a fortified site, it was important in the region until it was conquered by Moctezuma Ilhuicamina around 1465. Its pyramid beside a cliff and its great ballcourt are models of austerity and strength.
Veracruz
Golfo
1873
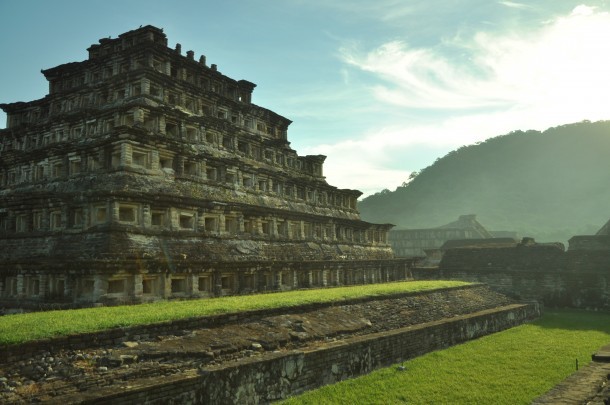
A majestic site with wide open spaces, numerous ballcourts and bas-reliefs, and particularly impressive for the Pyramid of the Niches, with its 365 niches, El Tajín has long been a source of fascination to specialists in Mesoamerican calendar systems and world view.
Veracruz
Golfo
1874
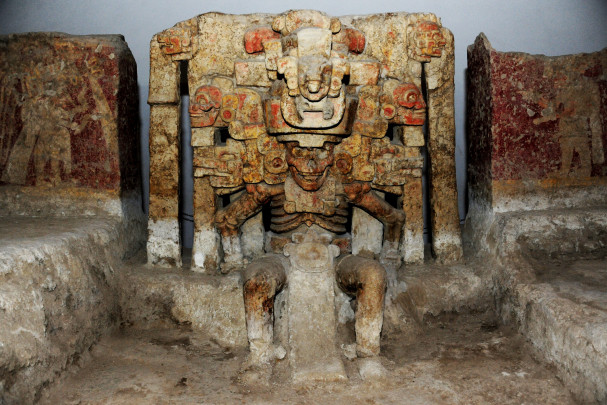
Mictlantecuhtli, the great lord of death (the other life), was the patron of the ancient Totonac city. The site museum’s most prized item is the sole unfired clay sculpture with stucco and the remains of paint in Mesoamerica. To this are added funerary offerings and ceramic figures of the very highest quality.
Veracruz
Golfo
14540
The greatest legacy of Totonac art. This site flourished between 600 and 900, and offers a unique insight into the development of the area's people through the astonishing murals of ritual scenes, temples, people, animals and symbols painted on the walls of its structures.
Veracruz
Golfo
1875
A Totonac settlement (900-1521 AD), with a marvelous view of the coastal plain. It came under the control of the Toltecs first and later the Mexica. In turn a city, a cemetery (78 tombs were found) and a fortress. This was where Hernán Cortés formed an alliance in order to conquer the Tenochca empire.
Veracruz
Golfo
1876
A very ancient and populous Olmec city. Strategically located along land and river transport routes. Enormous stone boulders were brought from the Sierra de los Tuxtlas, a volcanic mountain range, to make sculptures of colossal heads and thrones. The site began to be abandoned 29 centuries ago.
Veracruz
Golfo
1877