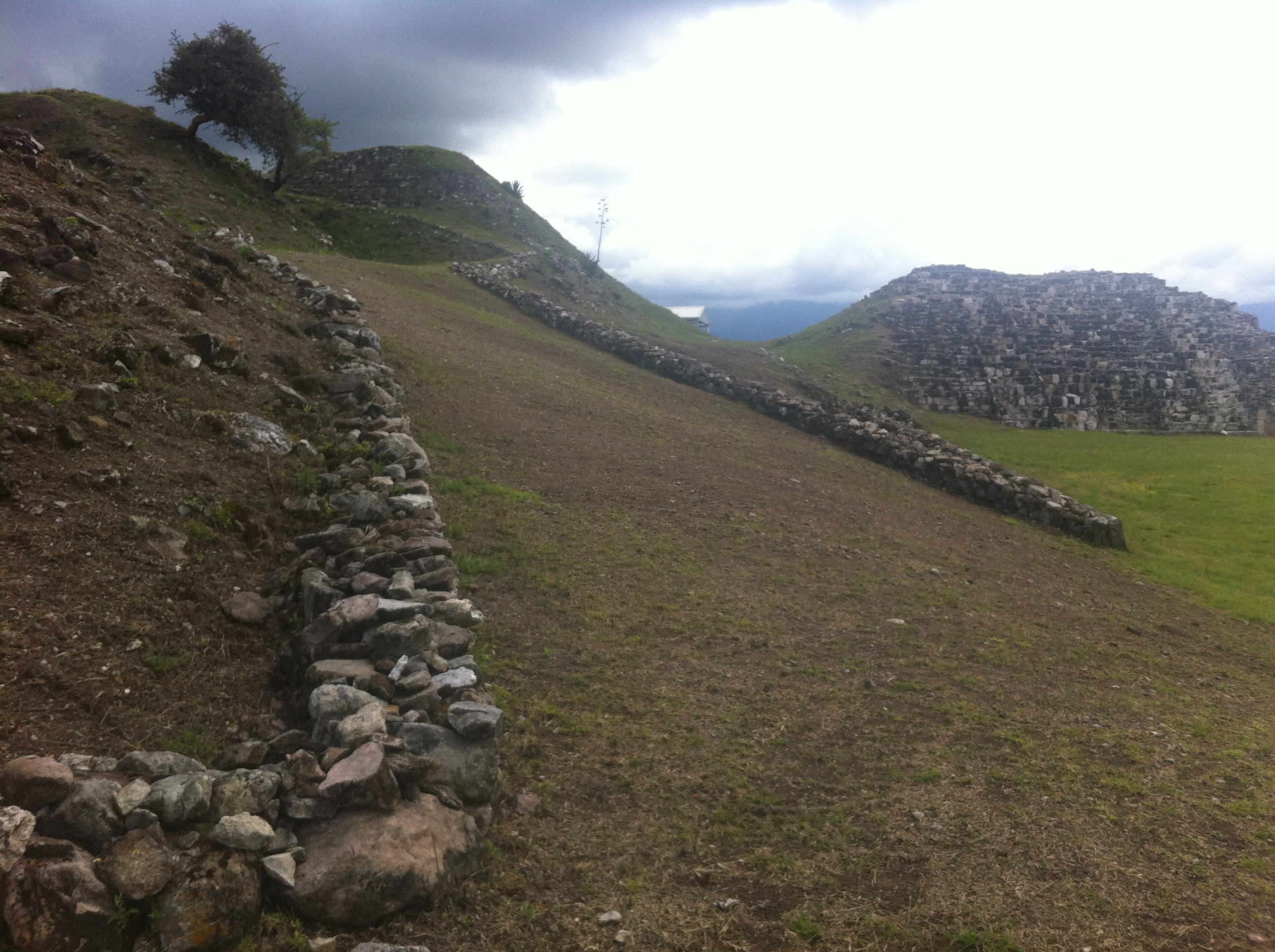
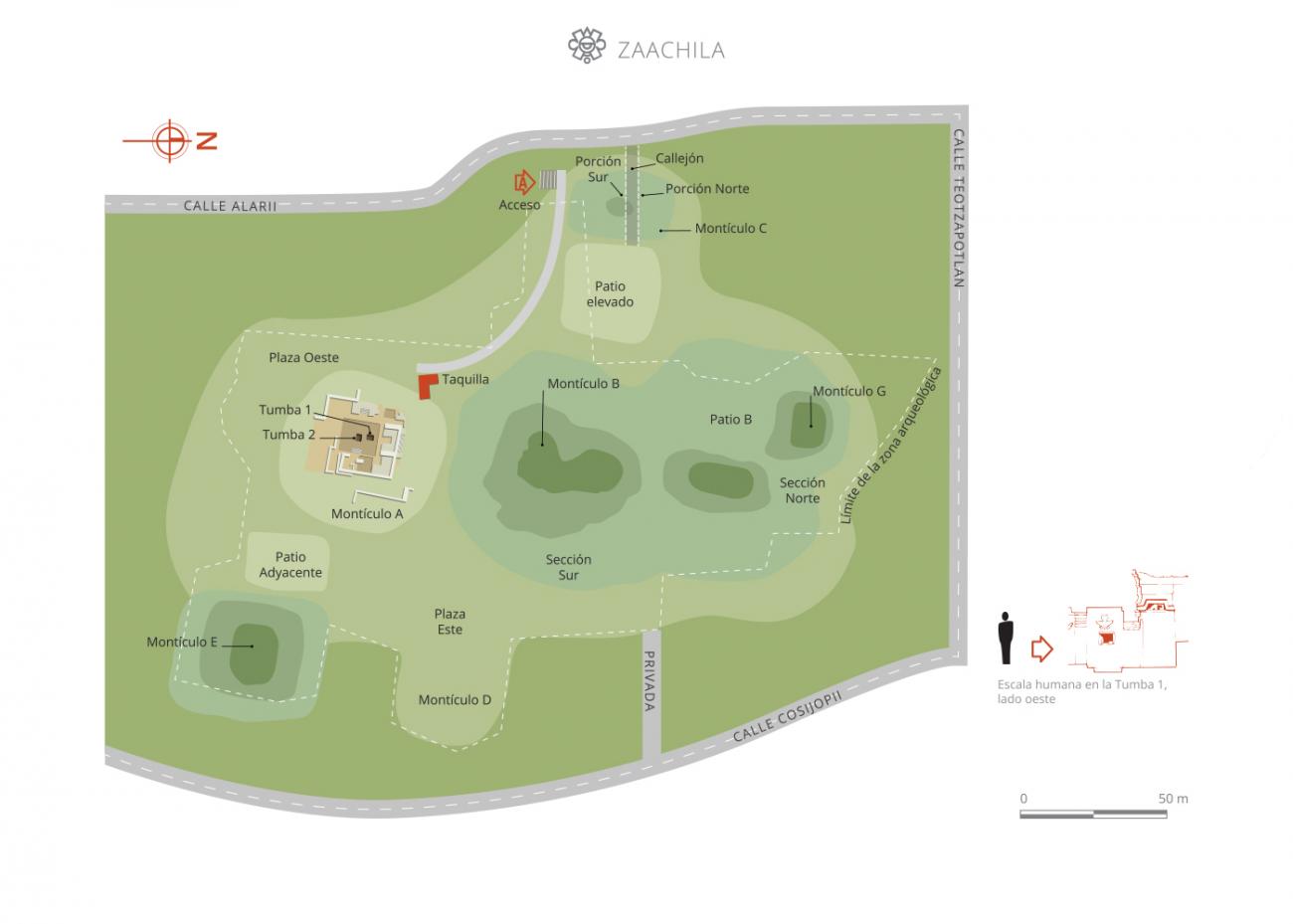
Zaachila belonged to the Zapotec culture and had 3,500 years of history. Around the Early Preclassic (1500-900 BC) it was a village with maize cultivation and a pottery tradition, where the inhabitants lived in houses made from sticks covered in clay. It was on the west side of the rocky island which is occupied today by El Cerrito, the principal archeological site. The area had a smaller population during the Middle Preclassic (900-100 BC) and the population fell around the end of this period (500-300 BC), possibly because its people moved and participated in the founding of Monte Alban. In the Early Classic (350-500) it was already a community with a mound and an estimated population of 315 people. Around the Late Classic (500-850) it was a great city-state, reaching an area of nearly 1,000 acres. In the Early Postclassic (850-1200), after the collapse of Monte Albán, Zaachila had a relatively large population while other centers were shrinking. In the Late Postclassic (1200-1521) it was a political center with a prominent lineage and a religious center alongside Mitla. Three of the tombs excavated are among the finest in Oaxaca. Finds include gold gems, carved bones, masks, turquoise disks and polychrome pottery. Around the mid-twelfth century there were royal alliances between the Zapotecs and Mixtecs. A daughter of the ruling family of Teozapotlan married a Mixtec noble from Almoloyas and from that date Mixtecs lived in Cuilapan.