Tamtoc
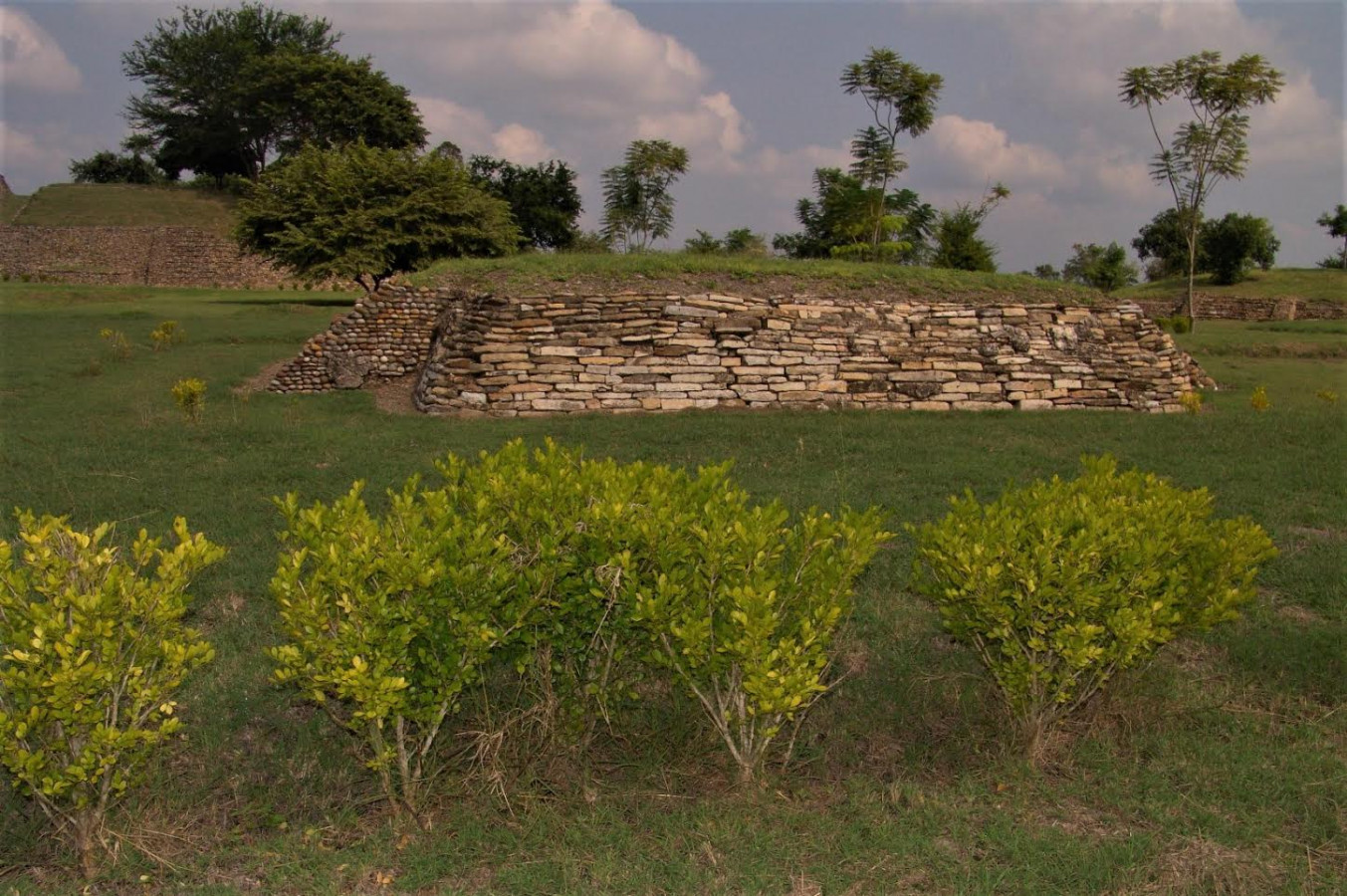
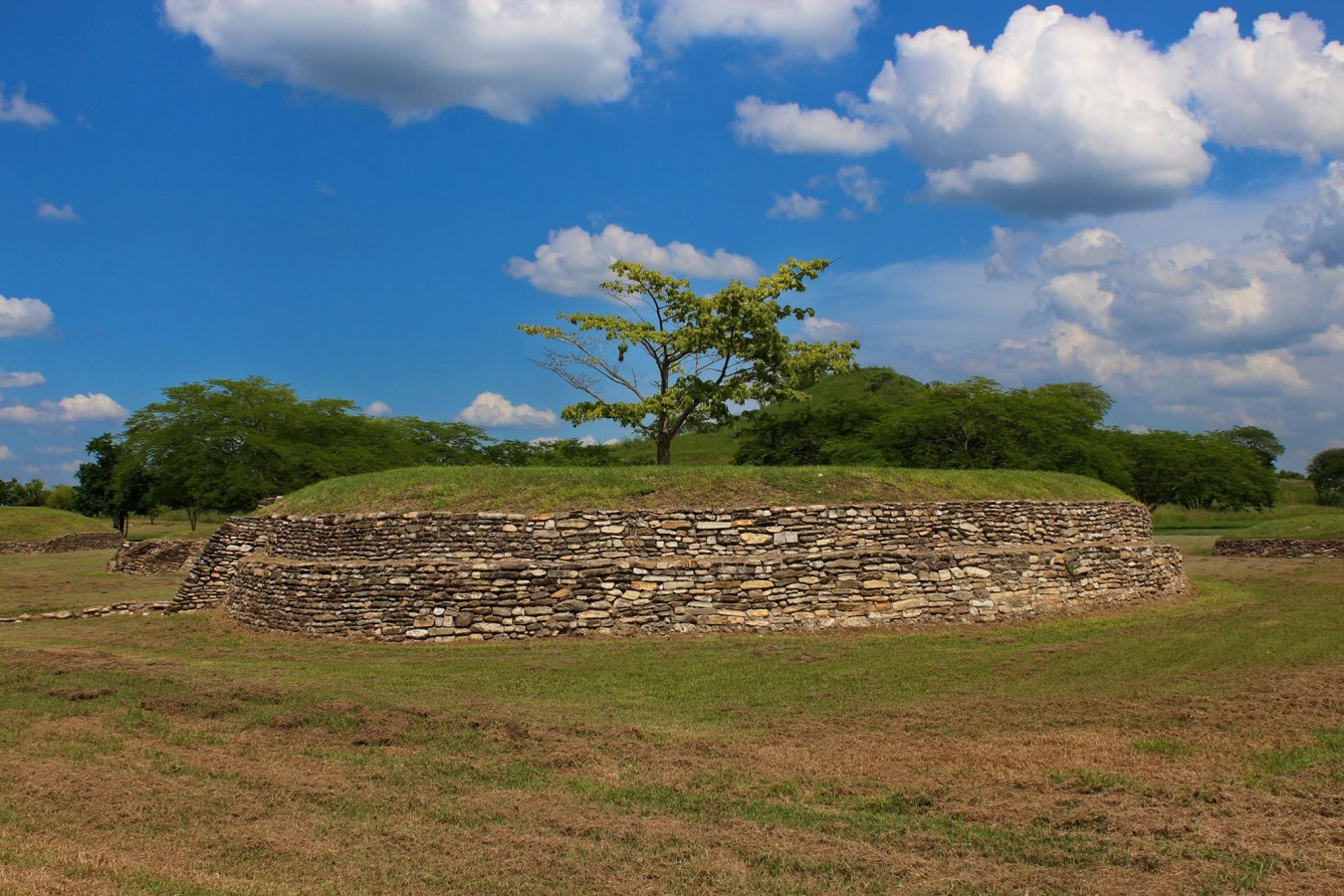
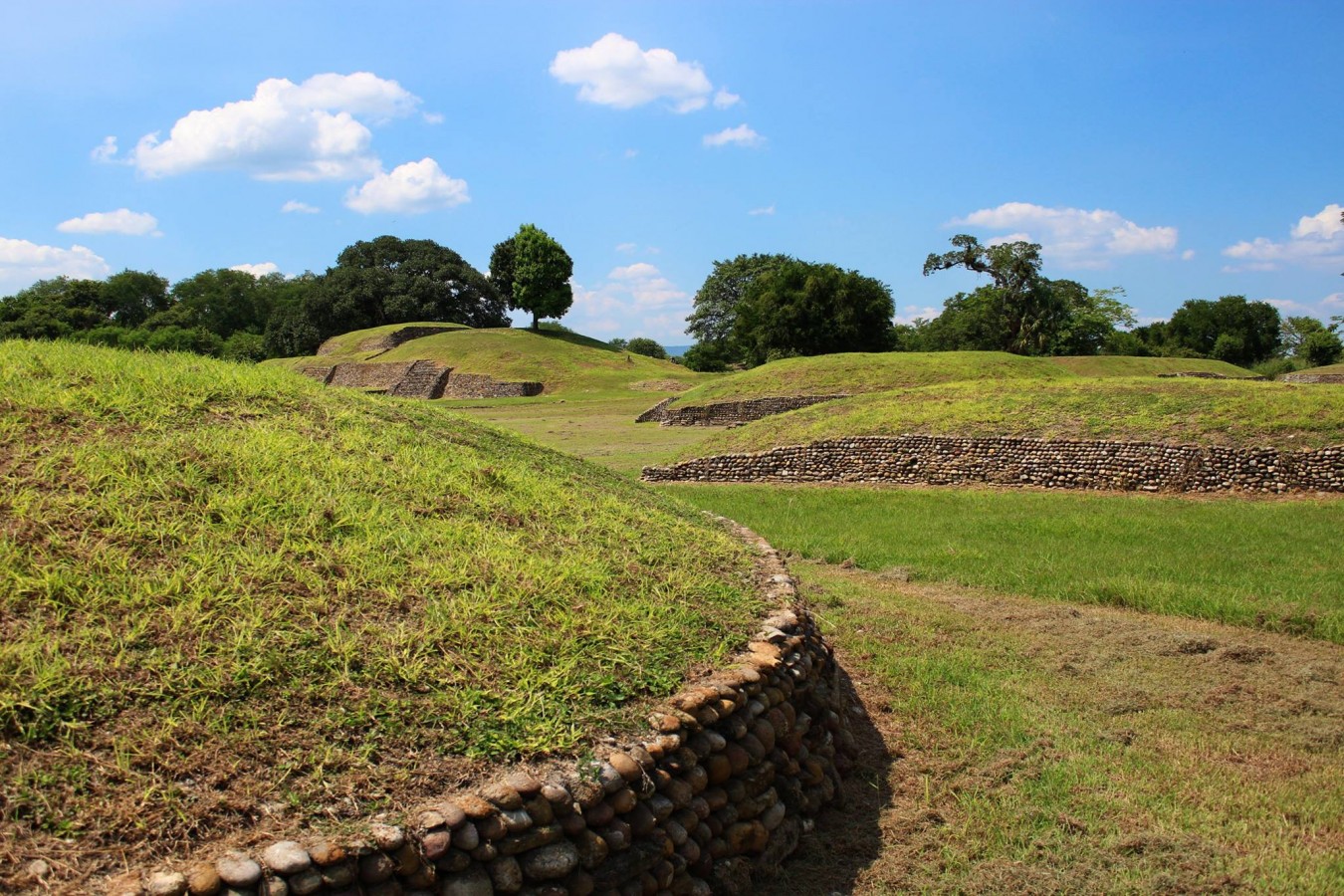
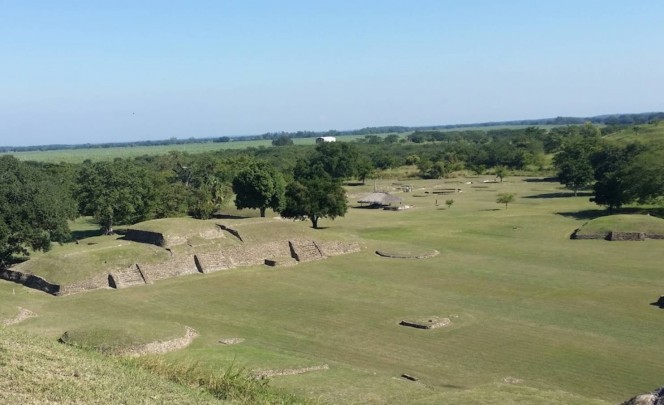
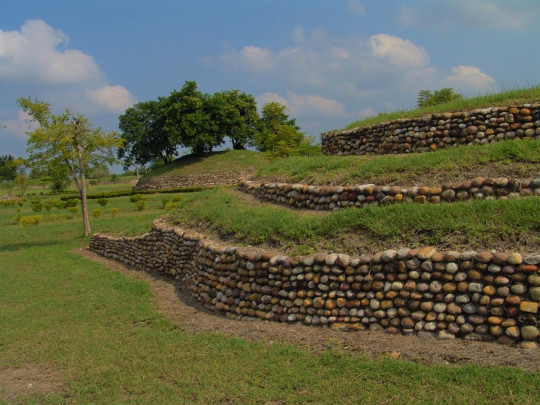
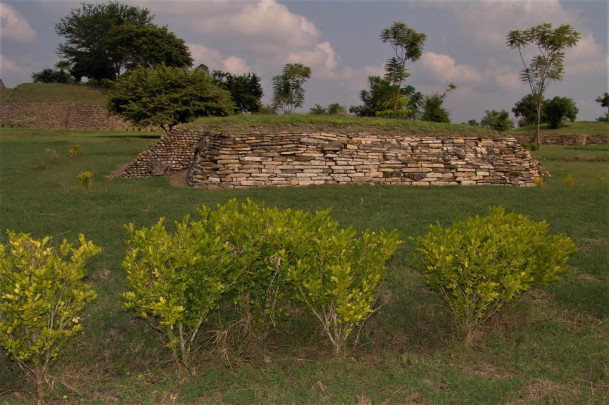
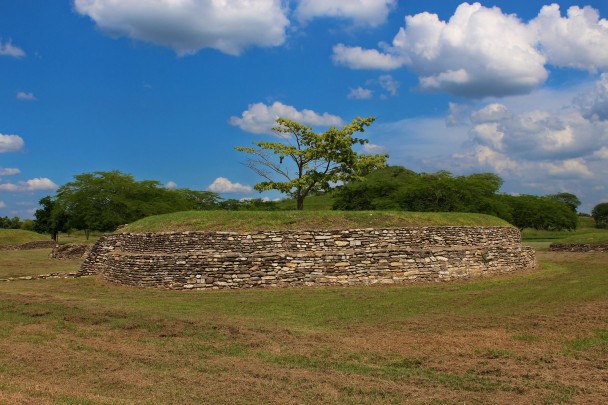
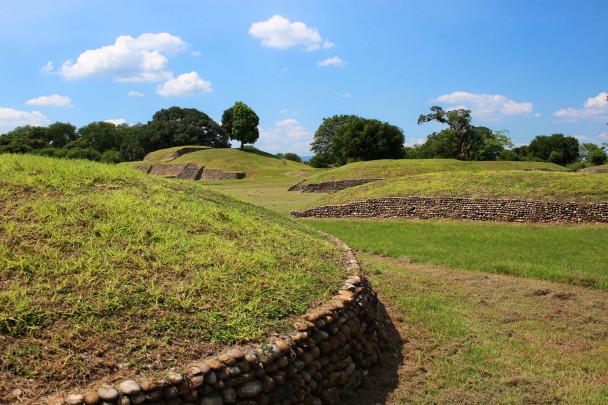
Located in the Huasteca Potosina region (900-1100 AD), with significant river trade, the site is remarkable for its pyramids, monoliths, stelae, mural paintings, the use of the calendar, circular buildings and amazing stone sculptures, such as the Venus of Tamtoc, which speaks of the important role of women.
About the site
For centuries, the ancient city of Tamtoc remained abandoned and hidden beneath dense rainforest until 1937, when the ethnology historian and archeologist Guy Stresser-Péan had the opportunity to carry out research work in the area; however, it was the engineer Joaquín Meade who made the discovery of the archeological site’s importance in 1942.
Meade was an expert on the Huasteca Potosina and his work is fundamental for any study of the region. In his publication "The Archeological Ruins of Huasteca Potosina" (1957), he mentions that, for their size, the pyramids of Tamtoc are the most significant in the area, and he describes the neighboring buildings and sites, as well as other discoveries.
At the end of the 1930s, the Museum of Archeology and Ethnology carried out work at various archeological sites in Huasteca, under the guidance of Enrique Juan Palacios and Wilfredo Du Solier. The latter worked on the El Consuelo site in 1946 (today known as Tamohí), during which period he carried out a few tours of the Tamtoc archeological site accompanied by Doctor Gordon Ekholm.
From 1962 to 1964, three seasons of fieldwork were carried out under the direction of Guy Stresser-Péan. This work included contributions from scientific consultants, technicians, restorers and engineers.
As a result, in 2001, the book “Tamtok Huasteco archeological site, its history, its buildings, vol. I” was published. The authors, Guy and Claude Stresser-Péan, presented the first results from this series of investigations relating to the historical and social evolution of the Tamtoc site. Later, in 2005, they published “Tamtok, Huasteco archeological site: daily life, volume II”, significantly contributing to the knowledge of the site's material culture.
In 1994, the archeologist Patricio Dávila, from the INAH Center in San Luís Potosí, resumed excavation work with the aim of understanding a number of aspects of the site’s architecture. Based on this intervention, in 2002 he wrote “Tantoc: a Huasteca city," and together with Diana Zaragoza, presented a number of lectures.
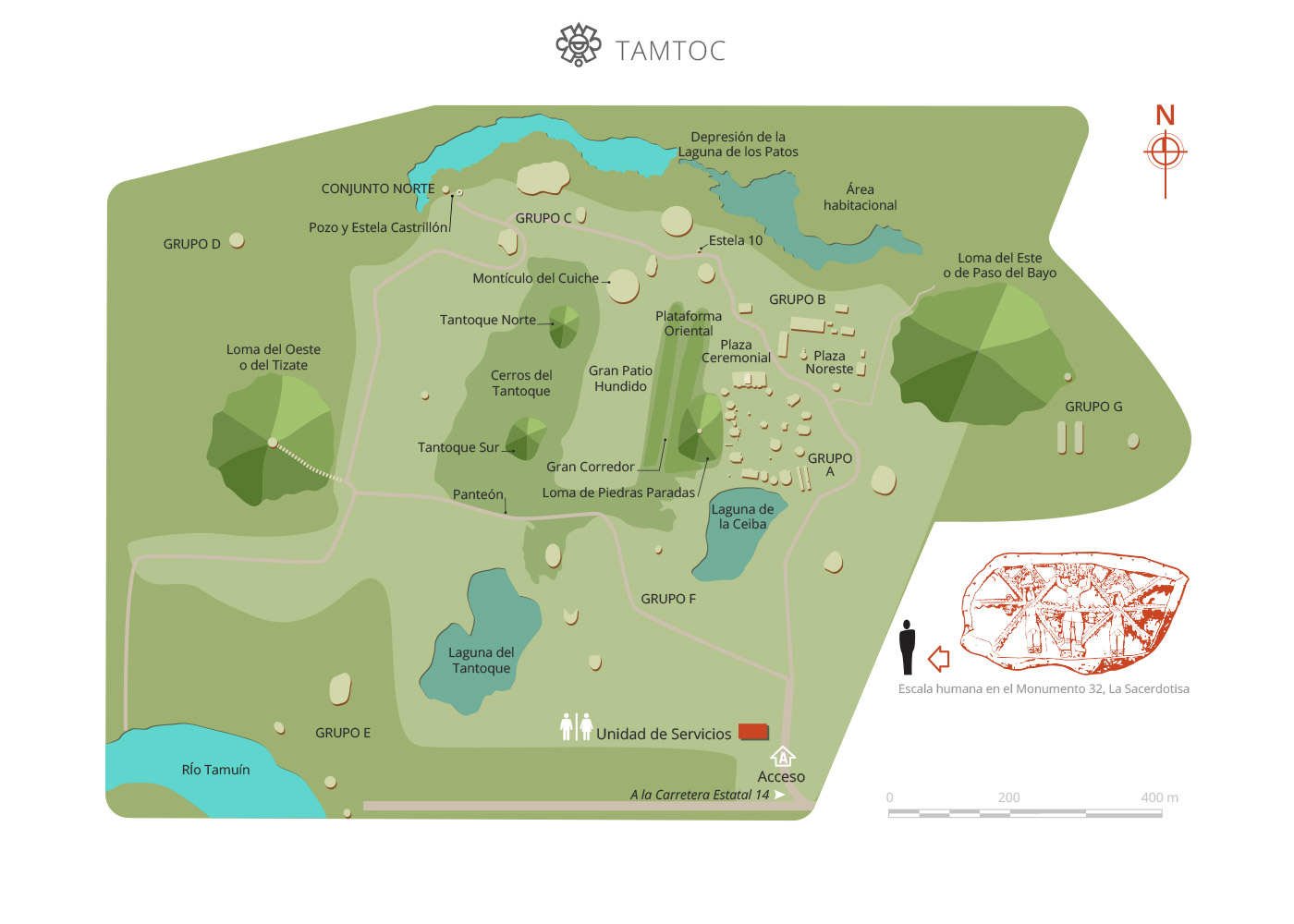
In 2001, the Tamtoc Archeology Project began again under the guidance of Guillermo Ahuja. It was financed by the Archeological Trust for the Recovery of Tamtoc, comprising the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH), the San Luís Potosí State Government and Banamex Cultural Development. During this period, further excavation and conservation of buildings were carried out. This included the exploration of the area of La Noria, particularly the recovery of Monument 32, the construction of the service area and the opening of the archeological site to the public in May 2006.
From October 2008 until the present day, the INAH has maintained the archeological project “Origins and Development of the Urban Landscape of Tamtoc, San Luís Potosí," with the participation of a group of specialists in various fields of anthropology who are interested in the study of the site, under the direction of Estela Martínez Mora.
Meade was an expert on the Huasteca Potosina and his work is fundamental for any study of the region. In his publication "The Archeological Ruins of Huasteca Potosina" (1957), he mentions that, for their size, the pyramids of Tamtoc are the most significant in the area, and he describes the neighboring buildings and sites, as well as other discoveries.
At the end of the 1930s, the Museum of Archeology and Ethnology carried out work at various archeological sites in Huasteca, under the guidance of Enrique Juan Palacios and Wilfredo Du Solier. The latter worked on the El Consuelo site in 1946 (today known as Tamohí), during which period he carried out a few tours of the Tamtoc archeological site accompanied by Doctor Gordon Ekholm.
From 1962 to 1964, three seasons of fieldwork were carried out under the direction of Guy Stresser-Péan. This work included contributions from scientific consultants, technicians, restorers and engineers.
As a result, in 2001, the book “Tamtok Huasteco archeological site, its history, its buildings, vol. I” was published. The authors, Guy and Claude Stresser-Péan, presented the first results from this series of investigations relating to the historical and social evolution of the Tamtoc site. Later, in 2005, they published “Tamtok, Huasteco archeological site: daily life, volume II”, significantly contributing to the knowledge of the site's material culture.
In 1994, the archeologist Patricio Dávila, from the INAH Center in San Luís Potosí, resumed excavation work with the aim of understanding a number of aspects of the site’s architecture. Based on this intervention, in 2002 he wrote “Tantoc: a Huasteca city," and together with Diana Zaragoza, presented a number of lectures.
In 2001, the Tamtoc Archeology Project began again under the guidance of Guillermo Ahuja. It was financed by the Archeological Trust for the Recovery of Tamtoc, comprising the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH), the San Luís Potosí State Government and Banamex Cultural Development. During this period, further excavation and conservation of buildings were carried out. This included the exploration of the area of La Noria, particularly the recovery of Monument 32, the construction of the service area and the opening of the archeological site to the public in May 2006.
From October 2008 until the present day, the INAH has maintained the archeological project “Origins and Development of the Urban Landscape of Tamtoc, San Luís Potosí," with the participation of a group of specialists in various fields of anthropology who are interested in the study of the site, under the direction of Estela Martínez Mora.
300 - 1100
Clásico Tardío a Posclásico Temprano
Preclásico Medio a Posclásico Tardío
900 - 1100
Clásico Tardío a Posclásico Temprano
Map
An expert point of view

Estela Martínez Mora
Centro INAH San Luis Potosí
Practical information
Sunday from 09:00 to 18:00 hrs. Last entry 17:00 hrs.
Free entry
Debido a las condiciones de la carretera, se recomienda respetar las indicaciones en el camino de acceso.
Se localiza a 17 km del municipio de Tamuín, San Luis Potosí.
Services
-
+52 (444) 813 4831
-
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Directory
Profesora Investigadora del Centro INAH San Luis Potosí
Estela Martínez Mora
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
+52 (044) 1487 9222