Las Pilas
Gets its name from a swimming place in a wooded area.
Surrounded by springs, its inhabitants were highly adept in the management of underground water and they built a complex system of channels for collecting and storing water. It was a site for the worship of water, with remarkable burials in the channels.
About the site
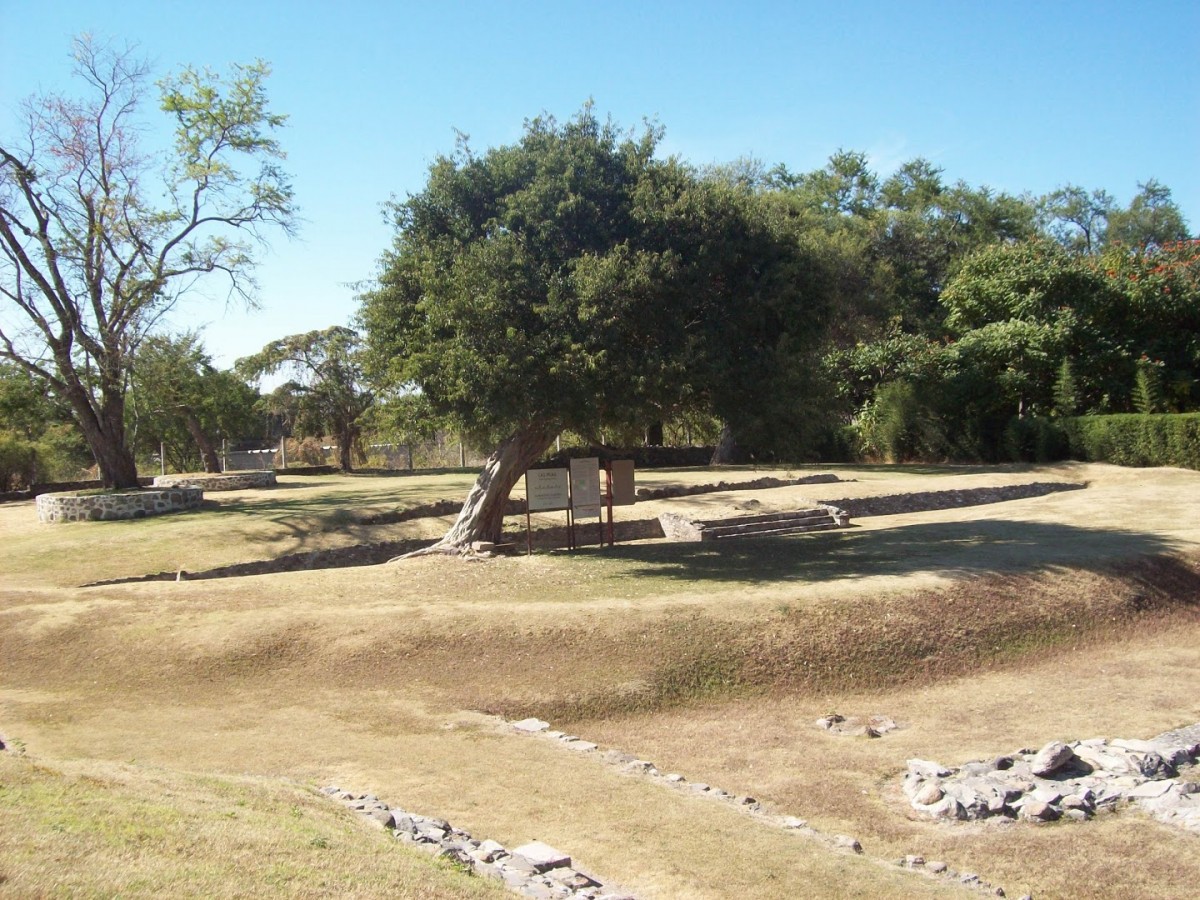
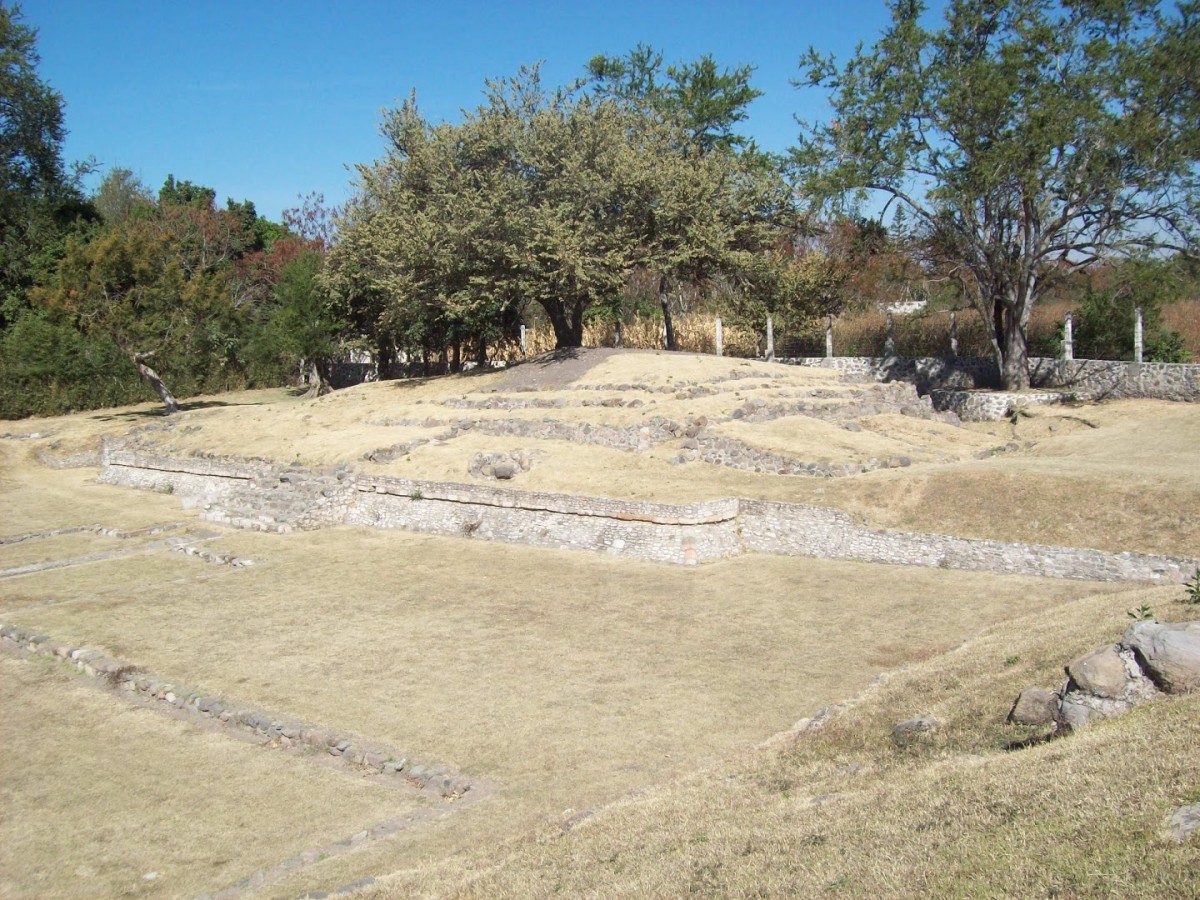
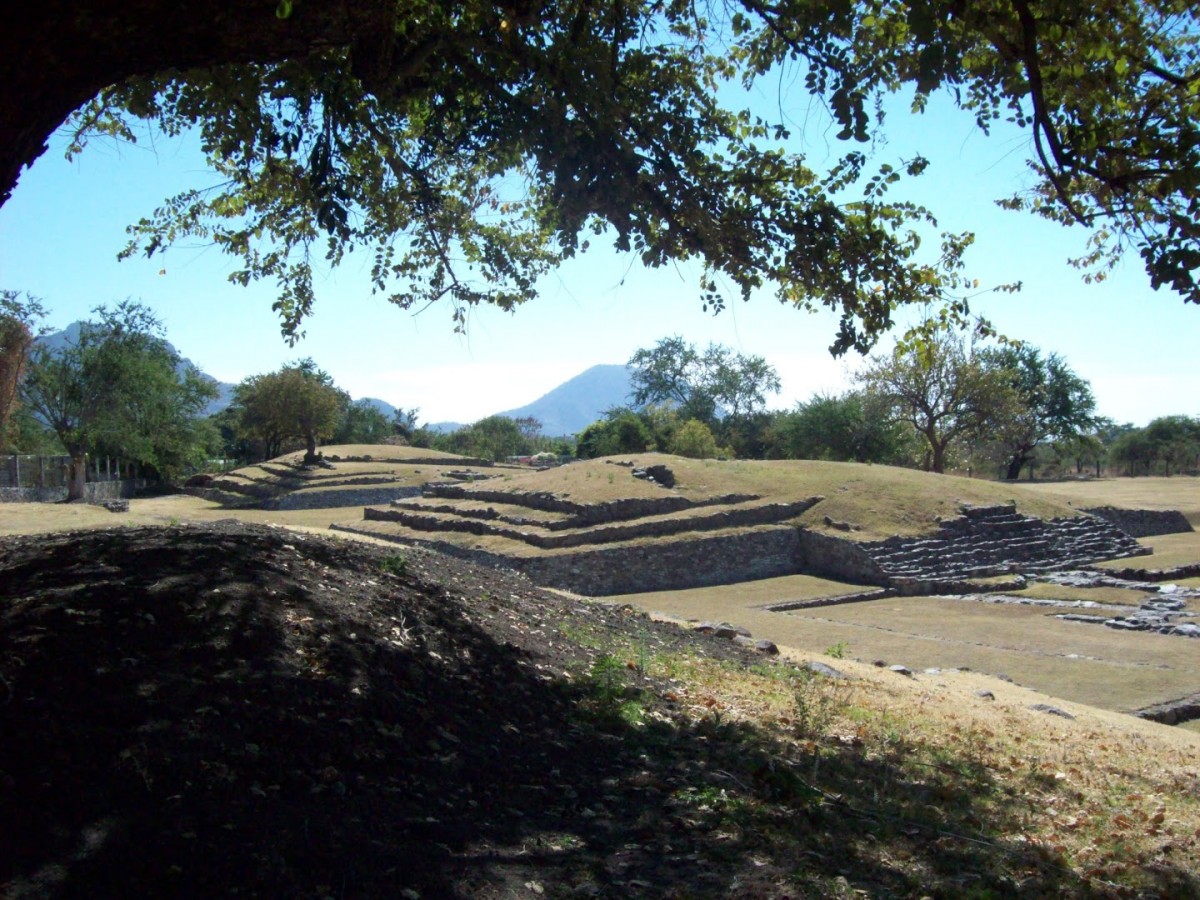
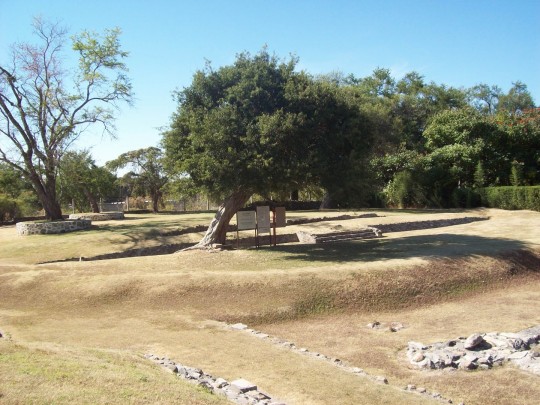
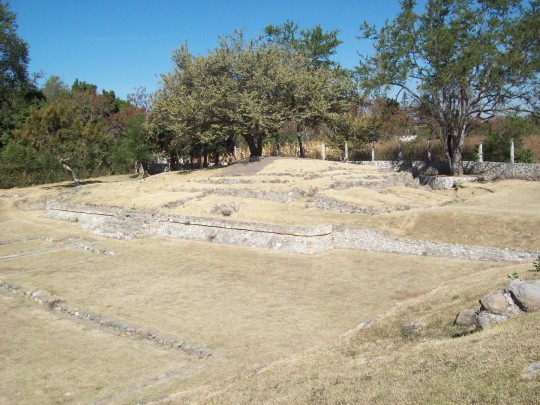
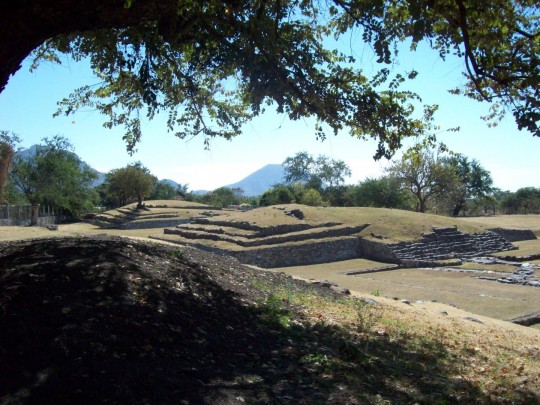
Urban sprawl has encroached onto the site of the archeological remains. The part which has been preserved was once a ceremonial area with six mounds from the period of Teotihuacan occupation. The four that have been excavated are divided into two areas known as Plaza A and Plaza B.
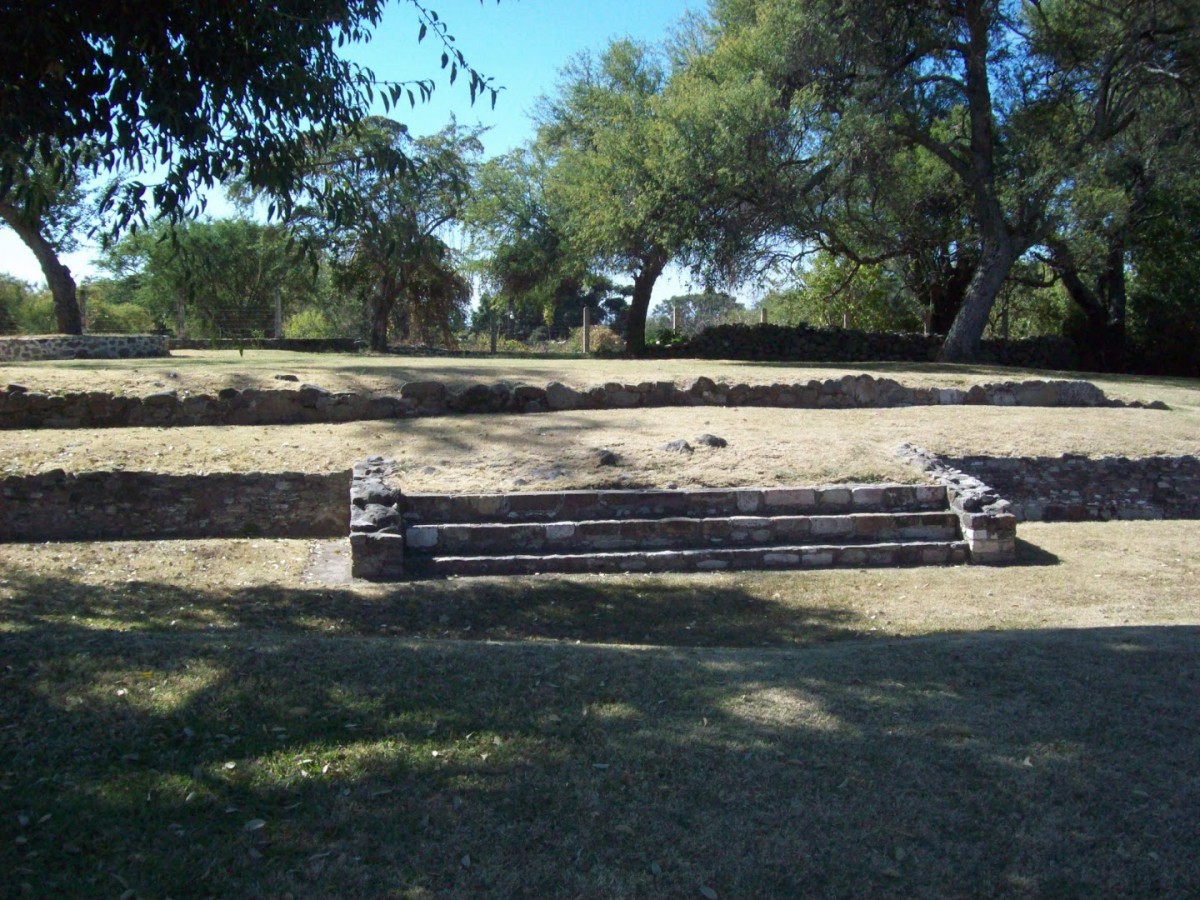
The size of these structures was reduced and architectural features were erased as a result of farming and settlement after the decline of the site. The only surviving evidence of this architecture, apart from stucco fragments, is part of the slab built into the slope of Structure 3 and the altar of Plaza B.
Water was fundamental to the physical development and belief system of Las Pilas. The two systems for water collection were fed by various springs in this area. The first platforms which gave rise to this ceremonial center were constructed at the same time as these systems, serving as the base for later construction, and enriched by the new ideas which arrived as a result of Teotihuacan’s expansion. Nevertheless, the discovery in the upper part of the first channel of an offering with two Preclassic pots similar to those at Chalcatzingo dates Las Pilas to an earlier period.
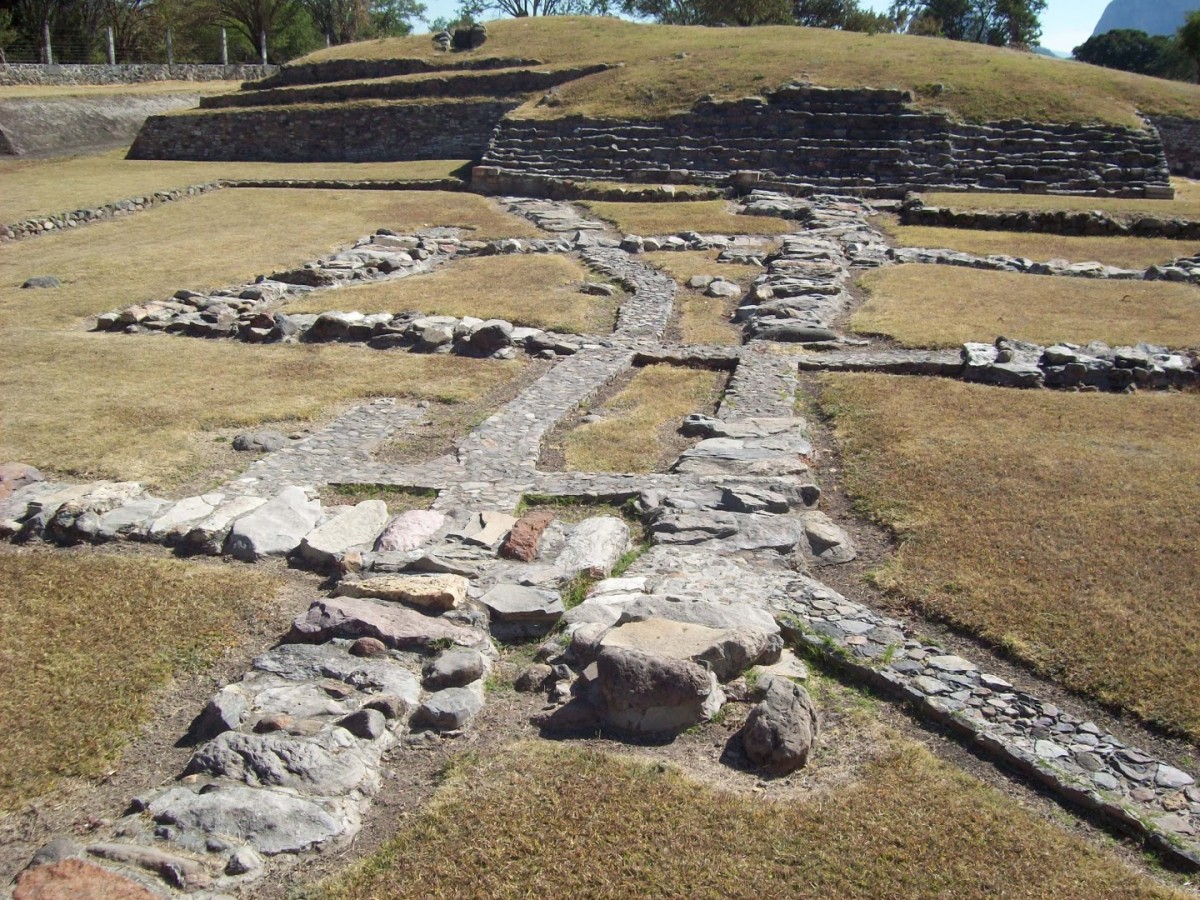
The second system is the more complex and better preserved of the two. It consists of two long channels which emerge from Structures 2 and 3, with other short ones converging at the former. They are constructed from river stones and are covered with slabs, taking water to a sedimentation chamber in the center of the plaza, with another channel leading to a cistern.
When the second system was abandoned, it became a burial ground for high ranking individuals. The bodies were placed within or at the sides of the channels with the legs in the lotus position and with abundant offerings. Notable among these is a pot bearing an effigy of Tlaloc and a number of cone-shaped figures with zoomorphic or fantastical heads, known as tepictoton or “conitos” (little cones). Fray Bernardino de Sahagún described them as representations of the mountains where the clouds were formed. They are currently on display in the Cuauhnahuac Museum of Cuernavaca. The three highest-ranking individuals were buried in a tomb close to the center of the plaza. The most important offering was a pendant representing Tlaloc, alongside bead necklaces and ear flares with hanging beads made from a blue-green stone.
The ceremonial center began to decline around 650 AD when Teotihuacan, its major center of influence, fell from power. Subsequently it became a temporary or permanent settlement used by various groups. In the early sixteenth century Jonacatepec is mentioned as paying tribute to the Mexica, and subsequently as the seat of government of a group of Tlalnahua towns.
During colonial times it was part of the marquisate of Hernán Cortés, and hence its importance was reduced to that of a center of evangelization and a stopping point for the mendicant orders on their route to Guerrero and Oaxaca. Sometime afterwards Jonatepec formed part of the sugar cane haciendas of Chicomocelo and Santa Clara Montefalco, until the restitution of irrigated and rainfed lands began by presidential decree in 1926.
The size of these structures was reduced and architectural features were erased as a result of farming and settlement after the decline of the site. The only surviving evidence of this architecture, apart from stucco fragments, is part of the slab built into the slope of Structure 3 and the altar of Plaza B.
Water was fundamental to the physical development and belief system of Las Pilas. The two systems for water collection were fed by various springs in this area. The first platforms which gave rise to this ceremonial center were constructed at the same time as these systems, serving as the base for later construction, and enriched by the new ideas which arrived as a result of Teotihuacan’s expansion. Nevertheless, the discovery in the upper part of the first channel of an offering with two Preclassic pots similar to those at Chalcatzingo dates Las Pilas to an earlier period.
The second system is the more complex and better preserved of the two. It consists of two long channels which emerge from Structures 2 and 3, with other short ones converging at the former. They are constructed from river stones and are covered with slabs, taking water to a sedimentation chamber in the center of the plaza, with another channel leading to a cistern.
When the second system was abandoned, it became a burial ground for high ranking individuals. The bodies were placed within or at the sides of the channels with the legs in the lotus position and with abundant offerings. Notable among these is a pot bearing an effigy of Tlaloc and a number of cone-shaped figures with zoomorphic or fantastical heads, known as tepictoton or “conitos” (little cones). Fray Bernardino de Sahagún described them as representations of the mountains where the clouds were formed. They are currently on display in the Cuauhnahuac Museum of Cuernavaca. The three highest-ranking individuals were buried in a tomb close to the center of the plaza. The most important offering was a pendant representing Tlaloc, alongside bead necklaces and ear flares with hanging beads made from a blue-green stone.
The ceremonial center began to decline around 650 AD when Teotihuacan, its major center of influence, fell from power. Subsequently it became a temporary or permanent settlement used by various groups. In the early sixteenth century Jonacatepec is mentioned as paying tribute to the Mexica, and subsequently as the seat of government of a group of Tlalnahua towns.
During colonial times it was part of the marquisate of Hernán Cortés, and hence its importance was reduced to that of a center of evangelization and a stopping point for the mendicant orders on their route to Guerrero and Oaxaca. Sometime afterwards Jonatepec formed part of the sugar cane haciendas of Chicomocelo and Santa Clara Montefalco, until the restitution of irrigated and rainfed lands began by presidential decree in 1926.
Did you know...
- INAH began the excavation of Las Pilas after intervening when a mound was destroyed to construct a swimming pool.
- The two water collection systems were similar, but the later one is better preserved.
- The stored water was used for irrigation to boost intensive farming.
- The site occupied the eastern side of the natural swimming spot, where there is still an ancient spring. For a number of years the spring supplied water to the town and this might be what gave the site its name.
- Mound 6, to the south, is on private land which was confiscated by a bank. It is in the process of being donated to the Morelos INAH Center.
Practical information
Wednesday to Sunday from 09:00 to 16:00 hrs.
$75.00 pesos
Se localiza en el municipio de Jonacatepec, al noroeste del estado de Morelos.
From the city of Cuautla, take the road that leads to Izúcar de Matamoros as far as the Amayucan junction, and take the exit for Atotonilco. The site is 2 km further on, within a bathing area.
Services
-
+52 (777) 314 4048
-
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Directory
Subdirector administrativo del Centro INAH Morelos
Salvador Castro Gómez
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
+52 (777) 312 3108